Theories of Intelligence
Personnel Theory of Intelligence
Aristotle propounded the view mind is comprised of various unmistakable and separate resources like memory, . As Human memory perception, focus, thinking, creative mind and discernment. These resources capability autonomously and they could be reinforced to work out. Be that as it may, this hypothesis has been refuted through tests.
Unitary Theory or Monarchic Theory
This hypothesis, the most seasoned in beginning, holds that knowledge comprises of one component, an asset of scholarly, he can use it in any circle of life circle of life and contingent upon it, be as fruitful in one circle as in some other. the thoughts proliferated by this hypothesis are not brought into the world out, in actuality, circumstances we can’t assume that the individual who is fruitful in field of craftsmanship can likewise be so in the area of science like math. Besides, an individual learned in dialects might find it challenging to manage mechanical nature of work. This shows that knowledge isn’t simply unitary variable thus unitary hypothesis isn’t satisfactory.
Spearman’s Two-Factor Theory (Electic Theory) or (G-Factor’ Theory)
English therapist Charles spearman (1927) contended that movements of every sort share one normal variable, called general knowledge, meant as ‘g’. It is characterized as a fundamental part hidden a wide range of scholarly capacities and making sense of connections among a wide range of insight measures. In any case, there are a few of ‘explicit capacities’ or ‘s’ variable might require pretty much of the g element and which give an individual the to manage explicit issues.
Accordingly, g (general knowledge) is basically the capacity fuel expected for different explicit capacities, the more fuel that is required, the grater the connection among g and s. In this outline, a considerable amount of general knowledge is expected for explicit capacity stamped S1, less for S2 and not very little for S3.
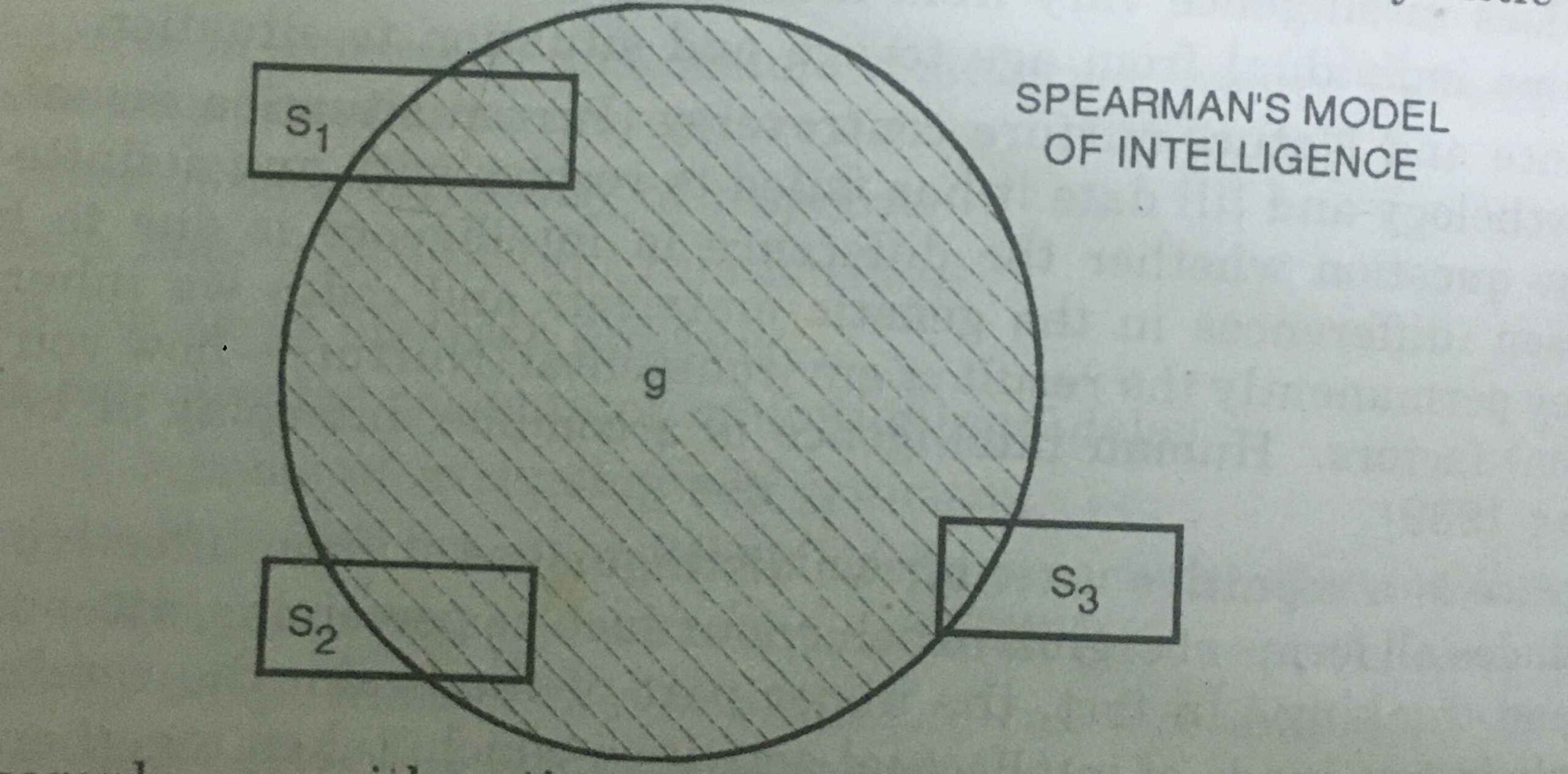
For model: a number-crunching test could tap, both G and a particular numerical capacity. Spearman’s perspectives are reflected in knowledge test eg. Raven’s Progressive Matrices, that yield a solitary score. Spearman put together his view with respect to the perception that individuals who scored high or low level on a comparable sort of trial of intelligence would in general score at on another tests, as well. Hence, those people who have and less of ‘s’ factor truly do genuinely well throughout everyday life.
G-Factor
It is a general, intrinsic capacity. It is a greater amount of ‘g’ factor an overall mental energy and stays steady in a person. Yet, it fluctuates from a person to person. A more prominent g factor implies a better progress in life since g-factor is utilized in all life exercises.
S-Factor
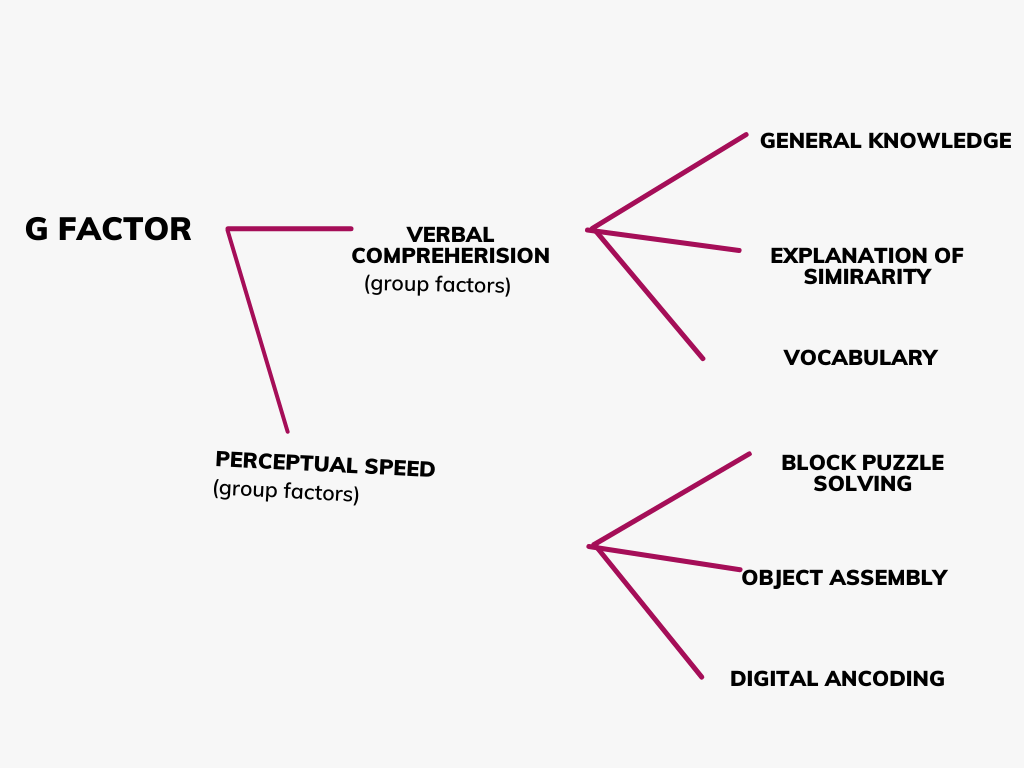
It is learned and that gained in the climate despite the fact that it is vital that the individual can possibly secure it. The s factor is basically the psychological energy which differs from one errand to another i.e. an individual might have explicit capacity for math and not for painting. Spearman later on added one more variable which is known as “Gathering gatherings of things inside a g-factor likewise connected with factor”.
for example gathering of things inside a g-factor likewise related with each other like in the element of verbal cognizance ; general information, g factor, clarification of similitudes and jargon connect with each other. In perceptual speed as a gathering factor, block-puzzle settling ,object get together and digit encoding relate with each other. Bunch factors are less broad, inescapable and homogeneous than ‘g’ element and more broad, boundless and homogeneous than ‘s’ factor.
Anarchic Theory of intelligence or Multifactor Theory
(E.L. THORNDIKE).This hypothesis was advanced by E.L.Thorndike. He didn’t trust in that frame of mind of general mental capacity. He was a connectionist and accepted that knowledge isn’t anything “however unambiguous upgrade – reaction association.” It believes insight to be a blend of various separate components or variables, every one being brief component of one capacity. There is no such thing as broad insight (g).
For example a solitary variable. As per this hypothesis, contrasts in knowledge among people are because of the number and sorts of associations that can be framed in the mind. Additionally, various undertakings can be achieved by numerous profoundly autonomous explicit capacities.
He recognized four essential ascribes of insight
(I) Level The degree of knowledge is corresponding to the degree of trouble of an issue soled. It can’t be estimated in amazing detachment.
(ii) Range : It alludes to the quantity of issues of a given degree that one can tackle. An individual having a specific degree of insight ought to have the option to take care of the entire scope of issue at that level.
(iii) Area : Area counts the complete number of circumstances at each level through which an individual can answer.
(iv) Speed This implies the snappiness on speed with which an issue is tackled. In any case, this hypothesis couldn’t be acknowledged as we can’t expect that with specific explicit sorts of capacities an individual would find success knowledge region and totally fruitless in different regions.
Group Factor Theory
L.L. Thurstone set forward the hypothesis that Intelligence is made out of a number of gatherings of firmly related capacities. He dismissed the thought that there is one general element that energize specific abilities. Thurstone, believed, what he called primary mental abilities, which is a small set of cognitive factors that together make up intelligence. While dealing with a trial of primary mental capacities, he came to the conclusion, that intelligence comprised of several group factors. (mental tasks that form a group because of common primary factor which gives them psychological and functional unity and which differentiate them from other mental operations). Thurstone, there are seven gathering factors, Namely;
(I) Verbal element (V). It is the capacity of grasping plans expressed in word. It can be defined as a factor in tests of such things as verval reasoning, reasoning by analogy and reading comprehension.
(II) Word familiarity (W). The capacity to talk or compose effortlessly or it is the office with words in exceptional settings like rearranged words, rhyming or naming whatever number words as would be prudent start with the letter V.
(iii) Numerical capacity (N). It is worried about the capacity to do estimations mathematical, quickly and precisely.
(iv) Spatial capacity (S). The capacity to control and imagine mathematical relations and comparative capacities intellectually.
(v) Associative memory (M). The capacity to cause arbitrary matched affiliations that to require repetition memory.
(vi) Perceptual speed (P). The capacity to get a handle on visual subtleties and to see contrasts and similitudes among objects.
(vii) General ability to think (R). The capacity to track down rules, standards ideas for understanding and tackling issues. Or on the other hand These capacities are viewed as generally autonomous of each other. However, relationships among these capacities are constantly observed to be positive which recommends that they are completely represented by an overall capacity somewhat.
Vernons‘ Hierarchial Theory
The British Psychologist, P.E.Vernon (1950) recommended that components of Gfactor hypothesis and the multifaceted speculations can be joined to shape a hierarchial hypothesis. In such a hypothesis, knowledge is imagined as a kind of pyramid. At the highest point of the pyramid is G, general knowledge, which appears in practically a wide range of scholarly movement. Under it are a few reasonably unambiguous capacity factors like Thurston’s essential mental capacities, named as VED and KM, addressing two primary sorts of mental capacities. While the principal significant gathering factor VED is worried about the verbal, mathematical and instructive capacities, the other significant gathering factor KM is worried about down to earth, mechanical, spatial and actual capacities. At the lower part of the pyramid are an enormous number of exceptionally unambiguous capacities, like spearman’s (1927) S factors capacities that might become an integral factor on one specific task.
Three-Dimensional or Three Factor Structure of the Intellect by Guilford
J.P. Guilford (1967, 1977, 1985) proposed a cubic model of the structure of intelligence. His model assumes that three separate factors make up any individual intellectual activity. These factors are
(i) “Operations” which refer to what the individual does such as remembering and evaluating.
(ii) “Contents” which refer to the material these operations such as symbols or on which 293 words. The “Products”. That results from applying individual (semantics) a particular performs
(iii) Products. That results from applying a particular operation to a particular content. The basic forms in which one can have information such as classes and implications.
Each one of these parameters-operations, contents and products may be further uh-dividend into some specific factors or elements. These factors were number total 120 in number with 5 kinds of operations, 6 kinds of products and 4 kinds of contents (5x6x4). Through his later researches, Guilford (1967) expanded his cube-shaped model of intellect include 150 factors (by dividing the figural factor in contents into 2 separate to Dories–visual & and auditory).
Hence, there are 5 x 6 × 5 = 150 factors in all, which may constitute human intelligence. Each one of these factors has a trigram symbol, i.e. at least one factor from each category of the three parameters has to be present in any specific intellectual activity on mental task.
To understand his theory, the help from a following task can be taken. The sentence, given a particular set of initial letters of the words.

Answers might be “we can eat nuts”. Here the individual creates (operation), meaningful but novel, sentences (products) using words (contents).
According to Guilford : Concept of intelligence, also includes what he calls divergent thinking which is closely related to creative or original problem solving, as opposed to convergent thinking, which is involved in solving problems with a single correct answer.
Cattell’s Theory of Intelligence
Cattell (1963, 1987) takes an integrated position on the general-versus-multiple-intelligence issue. He distinguished between two types of intelligence which though different and distinct, intermingle and interact to produce overall intelligence. According to his theory, intelligence is composed of two major components –
Fluid Intelligence. The ability to deal with new problems and encounters. It is considered to be the mental capacity of an individual, which is required for learning and problem solving. It is the ability to learn and perform in new and strange situation requiring adaptation, comprehension, reasoning, problem solving and identifying relationships. It is more intuitive and is active in forming new mental structure i.e. it is more creative and doesn’t take the help of already existing patterns of behavior. It is measured by tests of speed, energy and quick adaptation to new situation e.g., test of memory span, ability to copy symbols and ability to solve abstract problems. It declines with age after reaching full development by the end of an individual adolescence. It is derived from biological and genetic factors and not from training and experience.
Crystalized Intelligence. The store of specific information, skills, and strategies that people have acquired through experience. It is basically acquired knowledge i.e. it is learned through training and experience depending upon education and culture and is not innate or unlearned like fluid intelligence. It involves of general information consisting one’s acquired fund takes in one’s day-to- day of knowledge and skills essential for performing different life. It is measured by tests of vocabulary, social reasoning, problem solving, general knowledge of world affairs, handling of machines, craftsmanship and art, computation, the knowledge of customs ; traditions and to increase throughout one’s life span. rituals etc. It continues Thus, while crystallized intelligence is known for its intelligence is characterized by a relatively
A Triarchic View of Intelligence By Stenberg (1985, 1991)
A theory suggested that there are actually three kinds of intelligence, rather that a single factor that understand all intelligences or diversity of factors. this theory is comprised of three sub theories that serve as the governing bases for specific models of intelligent human behavior.
(i) Componential Intelligence. The ability to think to process information effectively. It analytically. It is the ability steps in the process involves mastering a sequence of components or of solving complex verbal, mathematical, or spatial reasoning problems. There are three information processing components, namely;(a) learning how to do things.(b) planning what things to do and how to do them.
(c) actually doing the things. People with highly developed componential intelligence often do well settings and score high on achievement in academic tests and standard I.Q. tests. However, such individuals do not show unusual creativity or insight.
(ii) Experiential Intelligence. The ability to formulate new ideas or to combine seemingly unrelated information. It involves learning from insight and experience. This kind of intelligence is best demonstrated when people are confronted with a novel situation
or are in the process of automating performance on a given task. Thus, to assess the degree of intelligence of an individual, he must be given an opportunity to perform new tasks or face novel
situations or problems. Those who have this component typical IQ tests, but they may are creative. Such ability is generally not score highest on predictive of success in a chosen field, be it business, medicine or carpentry. This is the kind of intelligence shown by many scientific geniuses and inventors, such as Alexander Fleming, Newton, Freud etc.(iii) Contextual Intelligence. The ability to adapt to a changing environment. Persons who are high on this dimension are intelligent in a practical, adaptive sense. This intelligence allows a person to find a good fit with the environment by changing one or the other or both. The test scores of such subject may not be high but they could come out on top in almost any context. Stenberg’s triarchic formulation is quite appealing in its broadness and in its recognition of practical abilities and skills that exist outside of the school room. Practical Intelligence- Intelligence related to overall success in living, rather than to intellectual and academic performance. Stenberg’s initial approach to developing a theory of what he calls “Practical intelligence focused on how people process information in order to solve problems and deal
effectively with their environments. He identified the following six steps of information process approach
-
- . Encoding- Identifying the key terms or concepts in the any relevant information from long term problem and retrieving
- Inferring- Determining the nature of relationships that exist between these concepts and terms.
- Mapping- Clarifying the relationship between previous situations and the present one.
- Application – Deciding if the information about known relationships can be applied to the present problem.
- Justification – Deciding if the answer can be justified
What is Spearman’s Two-Factor Theory of intelligence?
English therapist Charles spearman (1927) contended that movements of every sort share one normal variable, called general knowledge, meant as ‘g’. It is characterized as a fundamental part hidden a wide range of scholarly capacities and making sense of connections among a wide range of insight measures. In any case, there are a few of ‘explicit capacities’ or ‘s’ variable might require pretty much of the g element and which give an individual the to manage explicit issues.
What is Anarchic Theory of intelligence?
(E.L. THORNDIKE).This hypothesis was advanced by E.L.Thorndike. He didn’t trust in that frame of mind of general mental capacity. He was a connectionist and accepted that knowledge isn’t anything “however unambiguous upgrade – reaction association.” It believes insight to be a blend of various separate components or variables, every one being brief component of one capacity. There is no such thing as broad insight (g).
What is Group Factor Theory of Intelligence?
L.L. Thurstone set forward the hypothesis that Intelligence is made out of a number of gatherings of firmly related capacities. He dismissed the thought that there is one general element that energize specific abilities. Thurstone, believed, what he called primary mental abilities, which is a small set of cognitive factors that together make up intelligence. While dealing with a trial of primary mental capacities, he came to the conclusion, that intelligence comprised of several group factors. (mental tasks that form a group because of common primary factor which gives them psychological and functional unity and which differentiate them from other mental operations). Thurstone, there are seven gathering factors, Namely; Verbal element, Word familiarity, Numerical capacity, Spatial capacity, Associative memory, Perceptual speed, General ability to think
What are 5 important theories of Intelligence?
Intelligence is a term that has been defined in different ways. Even before psychology came into being philosophers dealt with intelligence and gave their about it. There is a good deal of controversy about the definitions opinions of intelligence. Intelligence is not knowledge though it is related to it in the sense that the amount of knowledge one can acquire is limited by his intelligence. Intelligence is not the same as talent. Five important theories of Intelligence are-Anarchic Theory of intelligence, Spearman’s Two-Factor Theory, Group Factor Theory , Cattell’s Theory of Intelligence, Three Factor Structure of the Intellect by Guilford.
