The Four Main Types of Psychology
During the current century psychology has made tremendous progress in its scope and field, psychology has circumscribed all aspects of human life. There is hardly any field of human behavior which is not affected by psychology in someway. The individual may be Men, Women, Child, Normal, Abnormal, human being or animal, bagger or businessmen, weather his behavior is moral or immoral, social or anti social, it becomes the subject matter of psychology to resolve these problems for which psychology have different branches. And the four main type of Psychology are: Clinical psychology, Cognitive psychology, Behavioral psychology, Biopsychology.
Four major types of psychology:
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Biopsychology
- Behavioral Psychology
Clinical Psychology
Clinical psychology describes and explain the causes of mental illness or abnormal behavior of a patient attending the clinic or hospital and suggest individual or group therapy for treatment and effective adjustment of the affected person in society.

Some of the main problems of this psychology are:
- Abnormality related to Emotion
- Abnormality related to cognition
- Abnormality related to psychodynamic function and social behavior like anti-social behavior.
Clinical psychology is an objective science in which problems are dealt by using various approaches like psychological, sociological, experimental and observational approaches
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology investigates all aspects of cognitive memory, thinking, reasoning, language, decision making and so on. for example, cognitive psychology has recently found evidence suggesting that the reason we cannot remember events that happen to us before we are about 3 years old is that we lack a clearly developed self concept prior to this age.
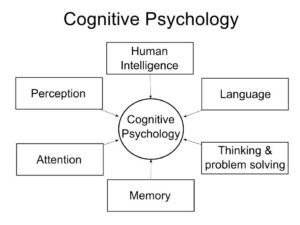
Cognitive psychology can be used problems such as:
- Anxiety disorders
- Personality disorders
- Depressive disorders
- Problems in daily life
- Stress management
- Substance abuse
- Thinking and problem solving
Behavioral psychology
Behavioral psychology suggest that environment shapes human or animal behavior. Any individual can be trained to perform any task regardless of where they come from and their internal thought process.
There are two main types of conditioning in behavioral psychology:
- Classical conditioning
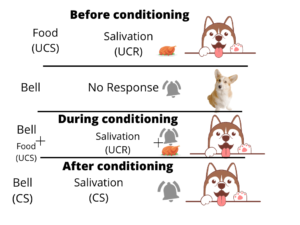
- Classical Conditioning is a procedure through which responses to stimuli are learned. Most people are familiar with conditioning even if they may not know the term itself.
- Pavlov’s experiment on a dog. A hungry dog was placed on a table standing but with slings under his body that prevented his walking away when the animal had become quite adjusted to this situation, an electric bell was rung and food was placed in his mouth, after the bell had been ringing for a certain time such as 15 sec. A few minutes later, the same sequence of stimuli was repeated the same after another pause and so on. After several repetitions the stimuli sequence bell-food-saliva began to flow. While the bell was ringing and before the food was given, the saliva began to flow with increased quantity. Thus, the salivary CR was established for that day. Again the experiment was repeated on next day, it was seen that saliva began to flow after few repetitions.
- Operant conditioning (also Known as instrumental conditioning
- In Operant Conditioning also as instrumental conditioning, organism learns to engage in certain behavior because of the effects of that behavior.
- Operant Conditioning organism engage in reinforcement behaviors that result in desirable consequences.
- There are two type of reinforcement-Positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement
- Positive reinforcement is a reward. it is a stimulus, like a piece of food, that we give to an individual to perform better in task and more likely to occur again in future
- Negative reinforcement are stimuli which strengthen a response when they are removed if the response occurs.
Biopsychology
Biopsychology is a branch of psychology that analyzes how biological, physiological, or genetics variables influence our behavior, thoughts, and feelings. This field of psychology is also known as biological psychology, physiological psychology, behavioral neuroscience, and psychobiology.
Biopsychology involves research on the brain, Neurons and Nervous system, Neurotransmitters, Hormones/Glandular system. It aims to explain human behavior from a biological standpoint.
It often focuses on :
- Sensory processes
- Learning and memory
- Motivation and excitement
- Cognition
Social Psychology
This branch of psychology deals with the group behavior and interrelationships of people with other people. Group dynamics, likes and dislikes, interests and attitudes, social distance and prejudices of the people in their personal and social relationships from the subject matter of this branch


Pingback: Motivation Meaning, Definition - PSYCHOFACTOR