THEORIES OF EMOTIONS
Emotions are seen to influence state, a number of physical us in many ways. When we are in an emotional change are seen. When perspiring, we become stiff and cold and our we see a ghost, we start eyes start falling out our body. When a young man sees the girl he loves, his heart start racing, he feels a tightness in his chest, he starts stammering besides other feelings.
These physical changes are controlled the central nervous system, affecting muscles, blood chemistry, by vessels, muscles of our organs as well as the adult human being the outward limbs and endocrine glands, blood even the iris of the eye. In an carefully hidden and perhaps signs accompanying emotions can be measured only might be controlled and instruments of the laboratory, like blood by the delicate pressure, pulse rate, extra measuring sugar in the blood.
JAMES-LANGE THEORY
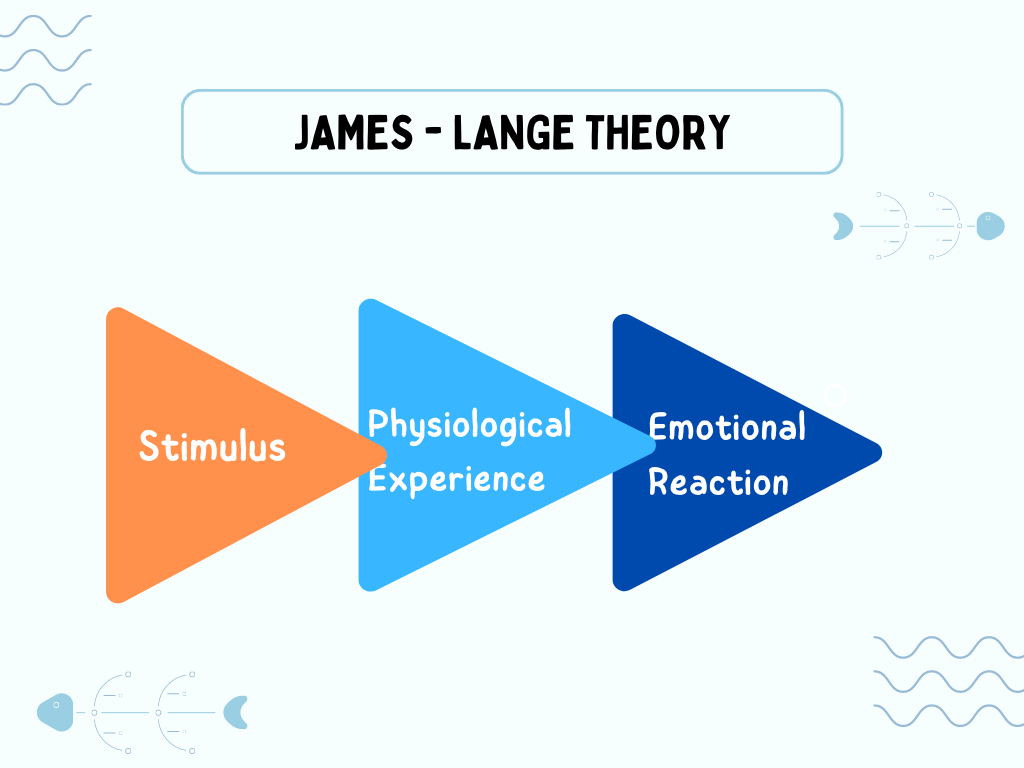
This theory of emotion totally changes the previous thinking about emotion. This was James and at the same time called James-Lange Theory. but actually proposed by William a Danish Psychologist Lange. When we are sad it is Common sense says that we are sad, scream because we are angry, run or tremble because we are afraid, James Lange said just opposite.
They said that we are sad because we perceive our self as shedding tears, when we see ourselves running and trembling we become afraid, and anger is aroused when we hear ourselves screaming. (It happens like this specific boost in the in the surrounding bring about physiological changes and these changes animate the different sensory never leading from various parts of the body to the brain. These messages are then perceived as emotion by the brain, The physiological changes come first arid the result of these changes in the motion.
For example: if you see a dog you will feel directly physical arousal (like trembling) along with that you will feel I am afraid and trying to run or it varies person to person.
CRITICISM
As per this theory every emotion should have specific bodily changes. But the experimental measurement of fear and anger display that the swapping are of a general process. It is extremely challenging to determine from physiological estimation alone what sort of feeling an individual is encountering.
Exactly the same individual, on two separate events when he mentions that he is feeling happy may show different bodily changes. Then, at that point, various individuals could show various examples while encountering a similar emotion. Some could sweat an extraordinary arrangement, others grate their teeth, and in others the pulse might shoot up when angry. So for these reasons the James-Lange Theory of emotion has not been accepted.
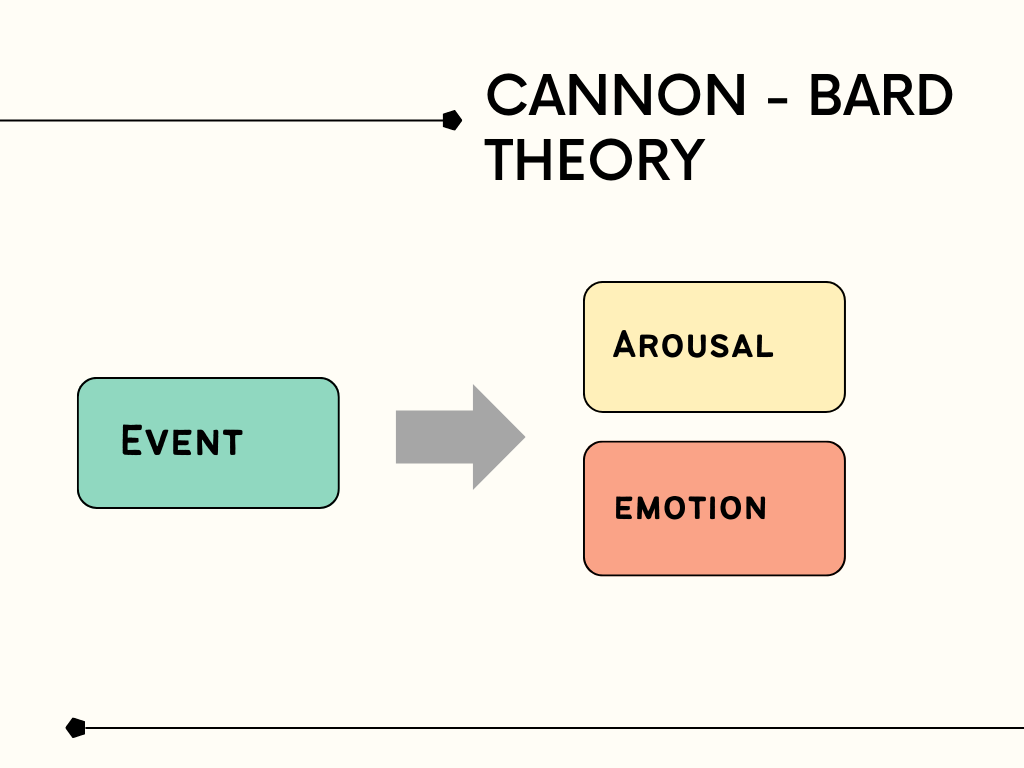
CANON- BARD THEORY
In the analysis of emotion. Canon looked for usual centers of emotion in the brain. He found that piece of the mind known as the nerve center was the significant focus of emotional activity. In his view, the cerebral cortex is the focal point of emotional experience. If an electrode is planted in an area can be made to behave as if it the hypothalamus of a cat, the animal was angry in the presence of enemy. In a dog ‘anger’ is produced if the entire cerebral cortex is eliminated.
In fact, he is more easily angered. This pattern continues if some other brain structures are also removed. According to this theory certain stimuli in the environment stimulate the hypothalamus which in turn activates the autonomic nervous system, which sets off the bodily changes in body which are associated with emotion. Simultaneously hypothalamus also sends messages of the sentiments to the cerebral cortex when the person is in emotion.
A lot of work is as yet going on the physiological, neurological and social viewpoints, of feelings. Additionally, on unambiguous inclination like apprehension, outrage, nervousness, and so on.
To conclude we may say that the emotional response has these components observable
- There is a behavioral pattern.
- There are clear side effects of physiological changes like the intersection of thoughtful sensory system, instinctive changes and excitement of the thalamus and nerve center.
- There is the inclination tone to each feeling which the individual alone can notice for himself.
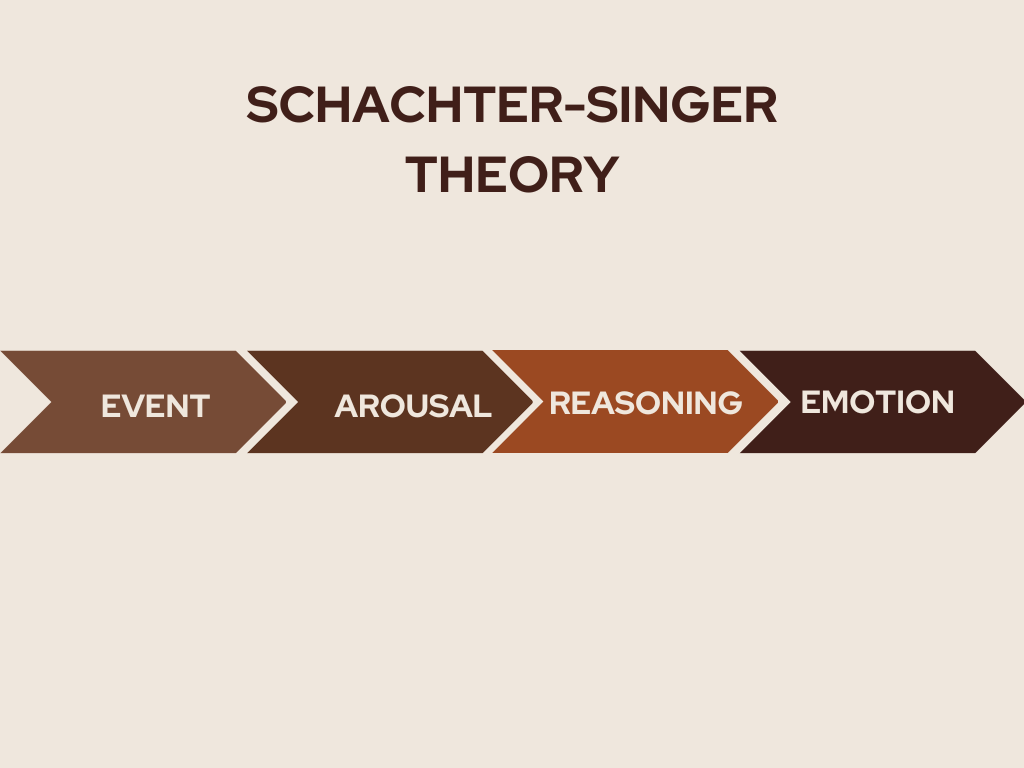
Schachter-Singer Theory
This theory of emotion was created by Stanley Schachter and Jerome E. Singer. Otherwise known as two-factor theory of emotion. Schachter-Singer’s theory of emotion suggested that emotion- provoking occasions produce internal arousal. Detecting this excitement, we concentrate on the outside climate to find the reason for its presence. The improvements we then notice lead us to choose a name for arousal. This, thusly, decides the exact feeling we see ourselves as encountering. In other word physical arousal and cognitive labeling take place simultaneously.
For example, A man got a new job and it is his first day while approaching work place he will find some physical changes (like increasing heart rate) here he will find out the reason behind it as using cognitive labeling. His heat rate is increasing because of nervousness or feeling afraid.
Cognitive Theory of Emotion
This theory was given by American psychologists Stanley Schachter and Jerome Singer white taking on the electric speculations of James Lange and Canon Bard in the year 1970. They proposed that our perception and judgment of circumstance (cognitive) mutually decide the feeling we feel.
At the end of the day we can say that emotional behavior change relies upon psychological changes and mental for cognitive understanding of these changes. One cannot work without the other. This view was additionally upheld by Magda Arnold. She involved the examination for the distinguishing proof and translation of emotion provoking stimuli.
Facial – Feedback Theory of Emotion
The facial- feedback theory of emotions proposes that facial expressions are connected to encountering emotions. Facial expressions re capable of affecting our emotions.
For example: if you are attending marriage and smiling at other you will automatically feel happy.
What is James-Lange Theory?
They said that we are sad because we perceive our self as shedding tears, when we see ourselves running and trembling we become afraid, and anger is aroused when we hear ourselves screaming. (It happens like this specific boost in the in the surrounding bring about physiological changes and these changes animate the different sensory never leading from various parts of the body to the brain. These messages are then perceived as emotion by the brain, The physiological changes come first arid the result of these changes in the motion.
What is Canon- Bard Theory?
Canon looked for usual centers of emotion in the brain. He found that piece of the mind known as the nerve center was the significant focus of emotional activity. In his view, the cerebral cortex is the focal point of emotional experience. If an electrode is planted in an area can be made to behave as if it the hypothalamus of a cat, the animal was angry in the presence of enemy. In a dog ‘anger’ is produced if the entire cerebral cortex is eliminated.
What is Schachter-Singer Theory?
This theory of emotion was created by Stanley Schachter and Jerome E. Singer. Otherwise known as two-factor theory of emotion. Schachter-Singer’s theory of emotion suggested that emotion- provoking occasions produce internal arousal. Detecting this excitement, we concentrate on the outside climate to find the reason for its presence. The improvements we then notice lead us to choose a name for arousal. This, thusly, decides the exact feeling we see ourselves as encountering. In other word physical arousal and cognitive labeling take place simultaneously.
What is Cognitive Theory of Emotion?
This theory was given by American psychologists Stanley Schachter and Jerome Singer white taking on the electric speculations of James Lange and Canon Bard in the year 1970. They proposed that our perception and judgment of circumstance (cognitive) mutually decide the feeling we feel.

Pingback: Emotion Meaning, Definition and Types - PSYCHOFACTOR